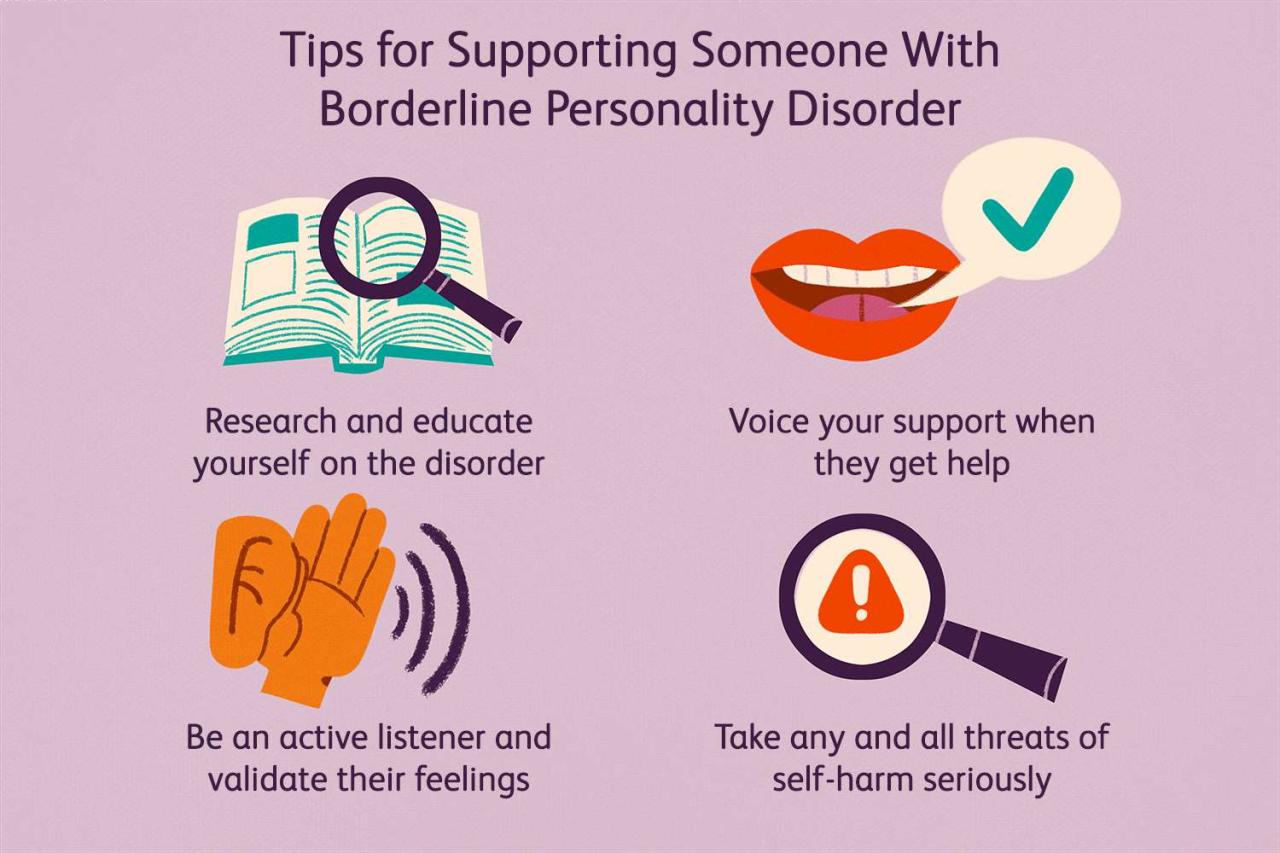
Borderline personality disorder, a complex and multifaceted mental health condition, takes center stage in this captivating discourse. Prepare to delve into the intricate world of BPD, uncovering its symptoms, causes, and effective treatment options. Our journey begins with a comprehensive overview of the disorder, laying the groundwork for a deeper understanding.
This discourse will navigate the complexities of borderline personality disorder, shedding light on its enigmatic nature. From its defining symptoms to the underlying causes and potential treatments, we will embark on an exploration that unravels the intricacies of this condition.
Symptoms and Diagnosis: Borderline Personality Disorder
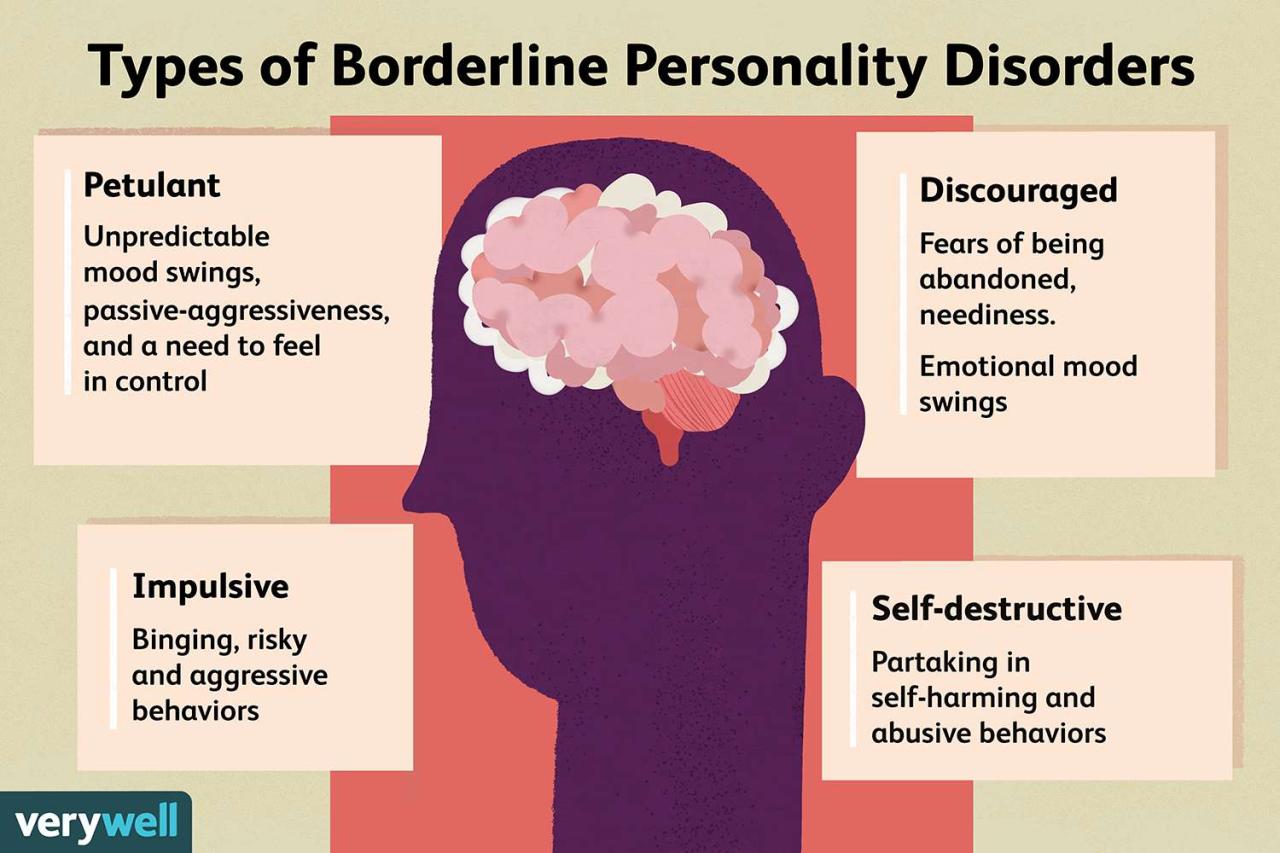
Borderline personality disorder (BPD) is a mental illness that affects how a person thinks, feels, and behaves. People with BPD may have difficulty controlling their emotions and may experience intense mood swings, impulsive behavior, and difficulty maintaining relationships.
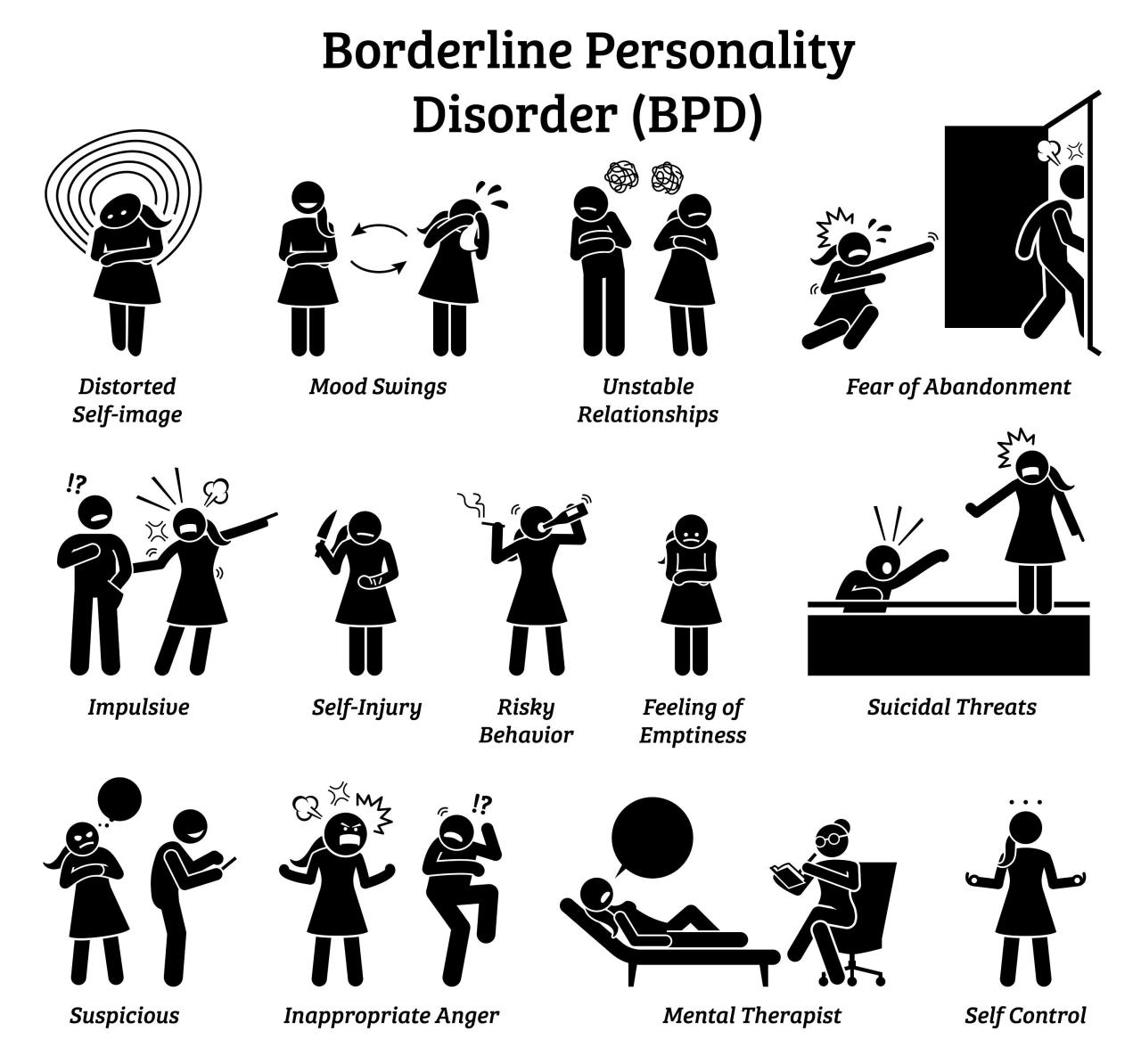
The symptoms of BPD can vary from person to person, but some of the most common symptoms include:
- Emotional instability:People with BPD may experience intense mood swings, from feeling extremely happy to feeling extremely sad or angry.
- Impulsivity:People with BPD may engage in impulsive behaviors, such as spending sprees, reckless driving, or substance abuse.
- Difficulty maintaining relationships:People with BPD may have difficulty maintaining healthy relationships due to their emotional instability and impulsive behavior.
- Self-harm:People with BPD may engage in self-harm, such as cutting or burning themselves.
- Suicidal thoughts or behavior:People with BPD may experience suicidal thoughts or engage in suicidal behavior.
BPD is diagnosed based on a person’s symptoms and a clinical evaluation. There is no single test that can diagnose BPD, but a mental health professional can use the following criteria to make a diagnosis:
- The person must have at least five of the following symptoms:
- Emotional instability
- Impulsivity
- Difficulty maintaining relationships
- Self-harm
- Suicidal thoughts or behavior
- The symptoms must have been present for at least a year.
- The symptoms must not be better explained by another mental illness.
Diagnosing BPD can be challenging, as the symptoms can overlap with those of other mental illnesses, such as bipolar disorder, depression, and anxiety. It is important to get a diagnosis from a qualified mental health professional to ensure that you receive the correct treatment.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of borderline personality disorder (BPD) is unknown, but it is believed to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Genetics
Studies have shown that BPD tends to run in families, suggesting that there may be a genetic component to the disorder. However, the exact genes that are involved have not yet been identified.
Environment
Environmental factors, such as childhood trauma, abuse, or neglect, are also believed to play a role in the development of BPD. These experiences can lead to changes in the brain that make it more difficult to regulate emotions and behavior.
Trauma
Trauma, particularly in childhood, is a significant risk factor for BPD. Children who experience trauma may develop BPD as a way to cope with the overwhelming emotions and experiences they have endured.
Other Risk Factors
Other risk factors for BPD include:
- Having a family history of BPD or other mental illness
- Being female
- Having a history of substance abuse
- Having a history of self-harm
- Having a history of suicide attempts
Treatment Options
Borderline personality disorder (BPD) is a complex mental health condition that can significantly impact a person’s life. Effective treatment can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Various treatment options are available, each with its own benefits and limitations.
Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy, or talk therapy, is a common treatment option for BPD. It involves working with a therapist to explore the underlying causes of the disorder, develop coping mechanisms, and improve interpersonal relationships.
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT): DBT is a specific type of psychotherapy designed to teach skills for regulating emotions, managing stress, and improving interpersonal relationships.
- Mentalization-Based Therapy (MBT): MBT focuses on helping individuals understand their own and others’ mental states, which can improve emotional regulation and relationships.
- Schema Therapy: Schema Therapy aims to identify and change maladaptive thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to BPD symptoms.
Medication
Medications can be helpful in managing certain symptoms of BPD, such as mood swings, impulsivity, and anxiety. However, medications alone are not sufficient to treat the underlying causes of the disorder.
- Antipsychotics: Antipsychotics can help reduce psychotic symptoms, such as hallucinations and delusions.
- Mood stabilizers: Mood stabilizers can help regulate mood swings and reduce impulsivity.
- Antidepressants: Antidepressants can help improve mood and reduce anxiety.
Other Treatment Options
In addition to psychotherapy and medication, other treatment options may be beneficial for individuals with BPD.
- Skills training groups: These groups provide a structured setting to learn and practice skills for managing emotions, relationships, and other challenges.
- Support groups: Support groups offer a safe and supportive environment where individuals can share experiences and connect with others who understand their struggles.
- Hospitalization: In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to provide intensive treatment and support.
Importance of a Comprehensive Treatment Plan, Borderline personality disorder
No single treatment option is effective for all individuals with BPD. A comprehensive treatment plan that combines psychotherapy, medication, and other support services is often the most effective approach. It is important to work with a healthcare professional to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses the individual’s specific needs and goals.
Last Recap
As we conclude our exploration of borderline personality disorder, let us reflect on the profound insights we have gained. This discourse has illuminated the complexities of BPD, empowering us with a deeper understanding of its symptoms, causes, and potential treatments.
By fostering awareness and encouraging empathy, we can create a more supportive and inclusive environment for individuals affected by this challenging condition.
FAQ
What are the hallmark symptoms of borderline personality disorder?
Borderline personality disorder is characterized by a range of symptoms, including emotional instability, impulsive behaviors, unstable relationships, and a distorted self-image.
What factors contribute to the development of borderline personality disorder?
The exact causes of BPD are unknown, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic, environmental, and psychological factors, including childhood trauma.
What treatment options are available for borderline personality disorder?
Treatment for BPD typically involves a combination of psychotherapy, medication, and support groups. Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) is a specialized form of therapy that has been shown to be effective in managing BPD symptoms.